Inserting data works much the same way as updating data using ORM.NET's Data Layer. In addition, updates and inserts can be handled by the same CommitAll() statement and involve separate and/or related table objects. In order to create a new object which will manage creating a new row within the database table the DataManager.New[Object] method is required instead of the Get[Ojbect] method.
The DataManager.New[Object] method assigns a new ADO.NET DataRow object reference to a local object which is then used to fill in the required data.
To create a new Student object and commit that data to the database you write the following:
C#
DataManager dm = new DataManager(Config.Dsn);
//assign a new object reference
Student s = dm.NewStudent();
s.FirstName = “Mike”;
s.LastName = “Smith”;
dm.CommitAll();
Visual Basic.NET
Dim dm As New DataManager(Config.Dsn)
//assign a new object reference
Dim s As Student = dm.NewStudent()
s.FirstName = “Mike”
s.LastName = “Smith”
dm.CommitAll()
The next example demonstrates creating both a Student and a Parent Contact object using the same CommitAll() method call. ORM.NET will generate the correct SQL statements to ensure that the new foreign key column FKContactId will be inserted into the Student record after the Contact record has been created.
C#
DataManager dm= new DataManager(Config.Dsn);
Student s = dm.NewStudent();
s.FirstName = "Tim";
s.LastName = "Brown";
s.Contact = dm.NewContact();
s.Contact.Address1 = "555 Main Street";
s.Contact.Address2 = "Apt 6";
s.Contact.City = "Oakland";
s.Contact.State = "CA";
s.Contact.PostalCode = "80304";
s.Contact.Country = "US";
dm.CommitAll(); // create both records and
// maintain the relationship between them in database
Visual Basic.NET
Dim dm As New DataManager(Config.Dsn)
Dim s As Student = dm.NewStudent()
s.FirstName = "Tim"
s.LastName = "Brown"
s.Contact = dm.NewContact()
s.Contact.Address1 = "555 Main Street"
s.Contact.Address2 = "Apt 6"
s.Contact.City = "Oakland"
s.Contact.State = "CA"
s.Contact.PostalCode = "80304"
s.Contact.Country = "US"
dm.CommitAll() ' create both records and
' maintain the relationship between them in database
ORM.NET ensures that all relationships will be maintained within the schema during updates, inserts and deletions.
Within each object class that is created by ORM.NET an Add[ChildObject] method is generated which requires a Child object to be passed in. The Add[ChildObject] method will create and associate a new Child record when CommitAll() is called.
The following example, creates a new Contact and a Child Student object using the Add[ChildObject] method.
C#
DataManager dm= new DataManager(Config.Dsn);
// Create new Student object
Student student = dm.NewStudent();
student.FirstName = "Cherry";
student.LastName = "Jackson";
// Create a new contact
contact contact = dm.NewContact();
contact.Address1 = "55 6th Avenue";
// add other contact information..
// Add the new Student to the new Contact object
contact.AddStudent(student);
dm.CommitAll();
Visual Basic.NET
Dim dm As New DataManager(Config.Dsn)
' Create new Student object
Dim student As Student = dm.NewStudent()
student.FirstName = "Cherry"
student.LastName = "Jackson"
'Create a new contact
contact contact = dm.NewContact()
contact.Address1 = "55 6th Avenue"
' add other contact information..
' Add the new Student to the new Contact object
contact.AddStudent(student)
dm.CommitAll()
In addition, a New[ChildObject] method is created for each child an object has defined. This offers a convenient way to assign an existing Parent object to a newly created Child object as shown below:
// find an existing Contact record
dm.QueryCriteria.And(JoinPath.Contact.Columns.Address1,"123 Main Street");
Contact contact = dm.GetContact(FetchPath.All);
Student student = contact.NewStudent(); // create a new Child object - Student
student.firstname = "Tom";
student.LastName = "Smith";
dm.CommitAll(); // CommitAll() will create a new Student object and relate it to the Contact
object
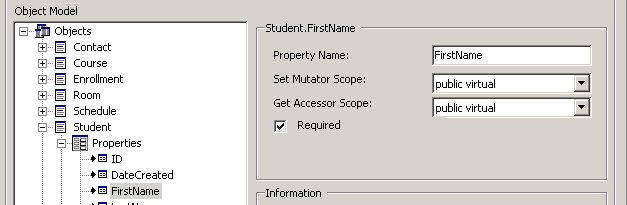
One of the settings that you can control using the ORM.NET Object Browser is whether or not a specific property (column) is required in order to create a new a object (row) .
For example, by enabling the Required checkbox within the Object Browser on the FirstName property, the NewStudent() method signature will be generated to require that a FirstName value is passed in.

The effect on the on NewStudent method once the Data Layer has been re-generated and compiled is shown below.
//FirstName is now required to create new Student object
Student s = dm.NewStudent("Mike");
//add a LastName value as well if you like...
s.LastName = Smith;
dm.CommitAll();
You can add as many object properties as you want to be required on the NewObject() method signature. Each required Property will be added to the New[Object] method as a parameter when the Data Layer is regenerated.
NOTE: Remember you will need to re-generate and then re-compile your Data Layer project after making these or any other changes to either the database or the database object model settings with ORM.NET.
NOTE: By default any column properties which do NOT Allow Nulls will have the Required checkbox enabled. However, columns defined as Primary Keys which are Identity or have Default value are implicitly “required” and ,therefore, you do not need to pass them in on a New[Object] method call.
In some cases it desirable to ensure that a new Parent object is created at the same time the Child object is. ORM.NET allows developers to control this by enabling the Required checkbox for that Parent within the ORM.NET Object Browser as shown below.
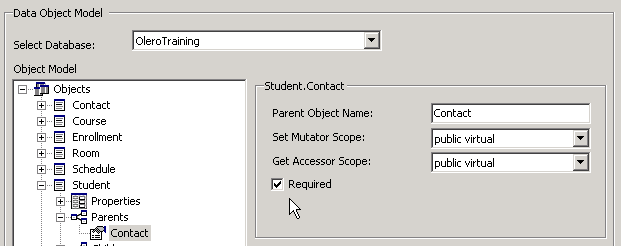
Once the Data Layer is regenerated and you recompile the solution the method signature for NewStudent() will now require a Contact object to be passed in.
C#
DataManager dm = new DataManager(Config.Dsn);
// create a new contact object with some information
Contact contact = dm.NewContact();
contact.Address1 = "123 Require Parent";
contact.City = "Boulder";
contact.Country = "US";
Student student = dm.NewStudent(contact); // Contact object is now required
student.FirstName = "John";
student.LastName = "Glass";
dm.CommitAll(); // Create the new Student and related Contact record
Visual Basic.NET
Dim dm As New DataManager(Config.Dsn);
'create a new contact object with some information
Dim contact As Contact = dm.NewContact()
contact.Address1 = "123 Require Parent"
contact.City = "Boulder"
contact.Country = "US"
Dim student As Student = dm.NewStudent(contact) 'Contact object is now required
student.FirstName = "John"
student.LastName = "Glass"
dm.CommitAll() 'Create the new Student and related Contact record
Both Properties and Parent objects can be required at the same time if desired. For example,
// A FirstName property and Contact object are now required to create a new Student object
Contact = dm.GetContact();
Student student = dm.NewStudent(“Tom”,contact);